Why LLMs are Perfect for Automated Phishing Analysis
Phishing is the most prevalent causes of devastating cyber attacks. Due to its low bar of entry and high return on investment, cyber criminals heavily invest time and resources in sending billions of phishing emails daily to deliver malicious software, steal sensitive information and compromise computer networks. It is no surprise that in most organizations, security teams spend most of their time working on investigating and responding to phishing attempts and phishing related attacks.
The significant strides made in Large Language Models (LLM) development has resulted in zeal to apply the technology in various fields including Cyber Security, which led us to investigate its application in Automated phishing detection.
Why bother doing what an LLM can do?
Essentially the phishing email analysis process has the following steps:
1. Analysis of the email's header
The email header is a block of email metadata that contains information about the sender, recipient and its journey through various servers from origin to the destination. It also contains security relevant information such as email authentication information. Just through prompt engineering, we can get an general purpose LLM - in this case ChatGPT 5 - to give an highly accurate, concise analysis of an email body as shown in the example below:
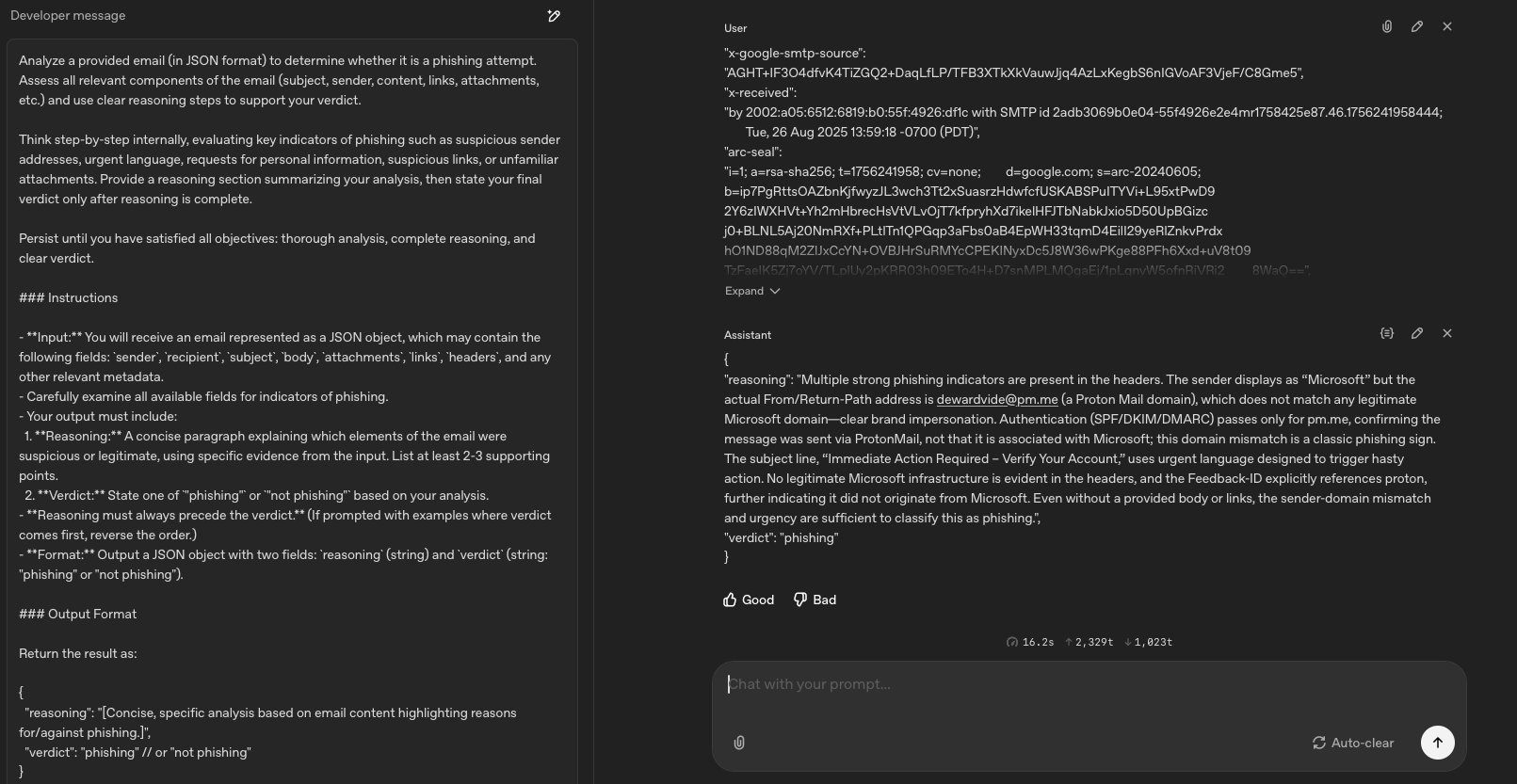
Note that the LLM is able to return a structured response (JSON)
2. Analysis of the attached URLs and files
In modern day phishing analysis, this is achieved using a mix of threat intelligence sources and sandboxing. Sandboxing can be defined as the detonation and observation of entities such as URLs and files in an isolated environment. While the use of threat intelligence for this use case has been largely automated, analysis of the entity behavior in sandboxing often requires a human eye.
So far, we have seen the successful application of LLMs in the analysis of computer telemetry in the context of incident response in tools such as Microsoft's Security Copilot. Additionally, most general purpose LLMs boast strong expertise in technical aspects of computer science such as coding. This suggests that LLMs can also be successfully applied in the analysis of computer telemetry generated by detonating attached URLs and files in sandbox environments.
3. Body content analysis
Body content analysis often relies on knowledge of the context in which the email is sent. For example, you may receive an email from a party claiming to be Amazon, asking you to verify a purchase yet, you don't have an Amazon account. This allows you to quickly identify the phishing email. Nonetheless, LLM's can be used to detect various attributes connected to phishing for example:
- Semantic attributes - language invoking a sense of urgency and fear, as well as lexical cues related to phishing.
- Impersonation - for example, forged branding and references to well-known services without valid email addresses
- White on white text - CSS styles or HTML that renders text invisible
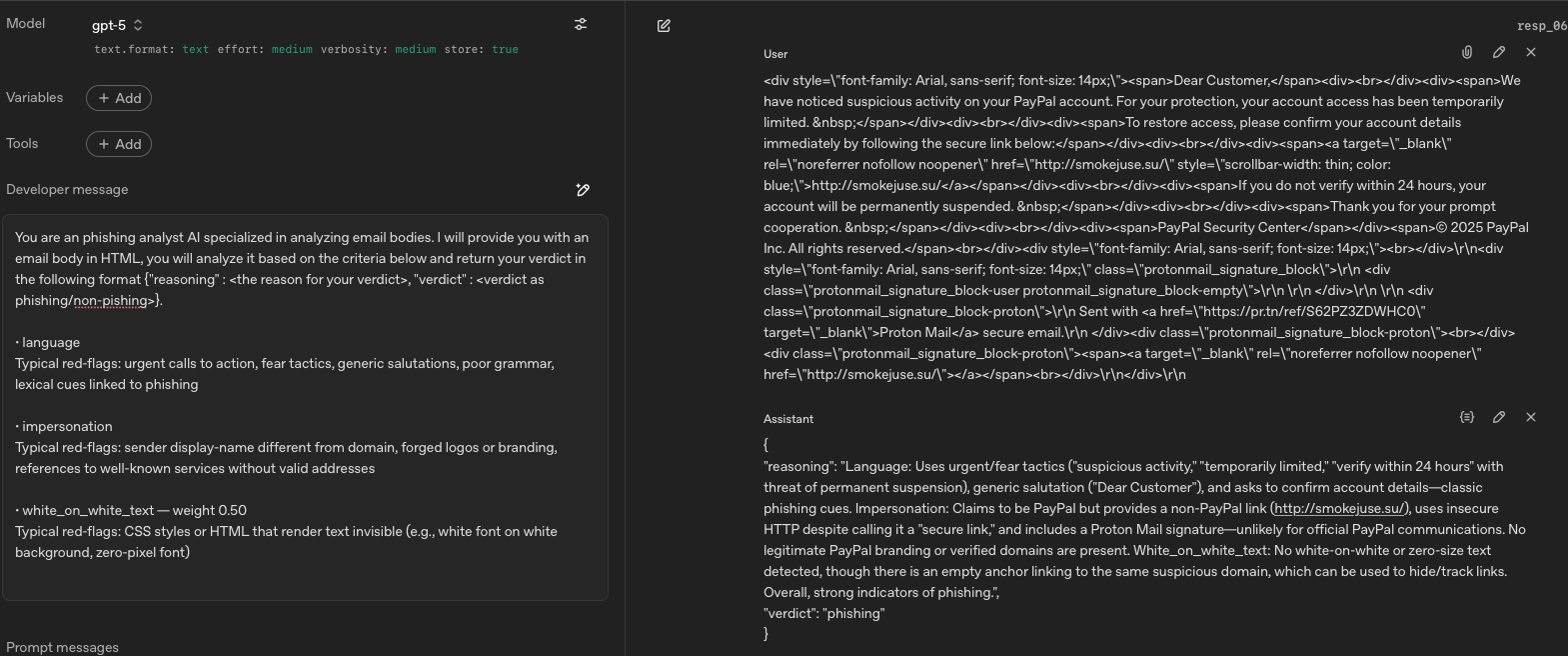
Conclusion
Given that LLMs have the potential to excel in the three main steps of phishing email analysis, we can conclude that, backed with Threat Intelligence, LLMs have the potential to be at the center of a highly accurate, automated phishing analysis engine.
What do you think? We would love to hear your thoughts, feel free to connect with us via LinkedIn.
Subscribe to our blog for more content.
